After long time waiting and reading lots of articles on how multi platform project can help reduce identical business logic in your app, i’ve decided to try out Kotlin Multiplatform Project for Android and iOS.
Why wait until now?
There are 2 reasons why i’ve decided to wait before start trying:
- There are no support for obj-c/swift generic before kotlin 1.3.40 https://blog.jetbrains.com/kotlin/2019/06/kotlin-1-3-40-released/
- I’ve found a reactive extensions for Kotlin Multiplatform called Reaktive https://github.com/badoo/Reaktive. Reaktive is different from RxKotlin as RxKotlin depends on RxJava, and cannot be used in multiplatform project.
Why not using Coroutines? some of you might say 😁. Well for starter, we already have couple of tutorials using Coroutines with Kotlin Multiplatform, and seconds, there are no reactive tutorial yet for multi platform project (as far as i know).
This tutorial provide an alternative approach building a multi platform project by using Reactive instead of Coroutines. This tutorial will take for about 1 to 2 hours of your time, prepare snacks and drinks a lot.
Enough with the talks, lets make our hand dirty.
Note:
- When reading this tutorial, bold word in between text means that you have to take a closer look.
- Italic sentences are additional informations that you can skip
Goal
Our goal is to make similar output and functionality on both Android and iOS by having the same business logic shared by Kotlin Multiplatform. This will be our final results:

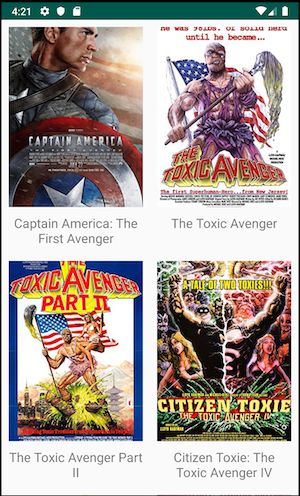
Note: you need macOS compatible platform to run Xcode
Approach
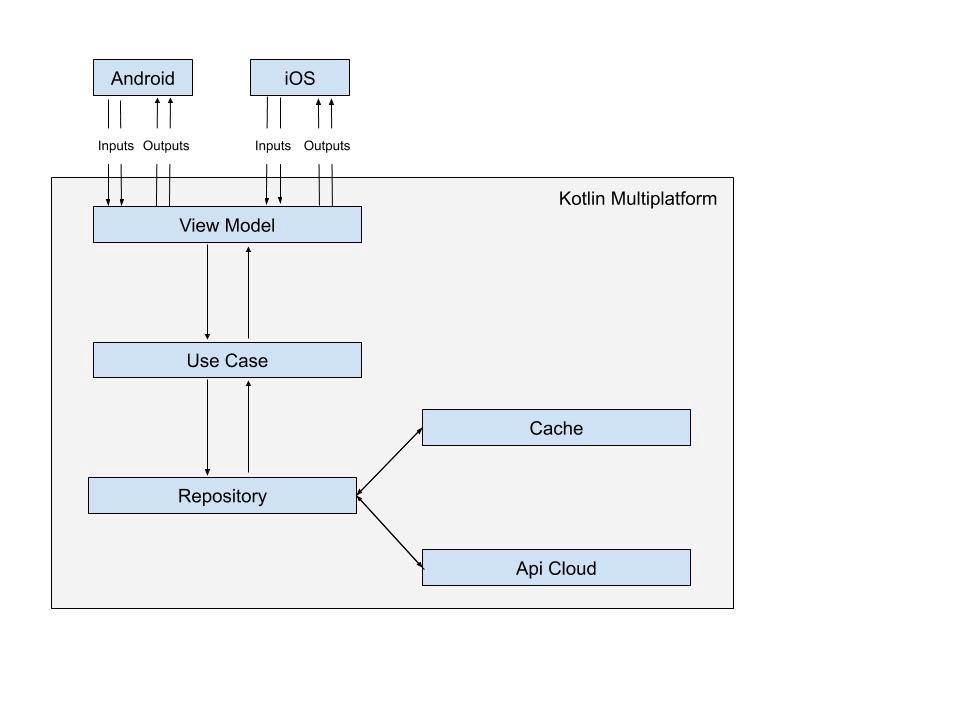
This tutorial will use MVVM with input output approach inspired by kickstarters, (https://github.com/kickstarter/native-docs/blob/master/inputs-outputs.md).
Here’s a design diagram how our app structure will be.
Libraries
At the time of writing, i am using the latest version of the following libraries:
- Kotlin, version: 1.3.50
- Reaktive, version: 1.0.0
- Ktor, version: 1.2.5, similar to retrofit for android / alamofire for iOS
- Sqldelight, version: 1.2.0
IDE
- Android Studio 3.5.1
- Xcode 11.0
Updates on Libraries (20 Sept 2020)
For those who are using Kotlin 1.4.0 and above, i’ve updated the sample on Github. Just checkout on branch Kotlin1.4.0
Updated libraries:
- Kotlin, version: 1.4.10
- Reaktive, version: 1.1.17
- Reaktive Coroutines Interop, version: 1.1.17-nmtc
- Ktor, version: 1.4.0
- Sqldelight, version: 1.4.3
- Coroutines: 1.3.9-native-mt
Please note there’s still issue with multithreading on K/N, so make sure you’re using Coroutines version 1.3.9-native-mt and not the 1.3.9 one.
Please also take a look on this issue regarding multi-thread coroutines:
https://github.com/Kotlin/kotlinx.coroutines/blob/native-mt/kotlin-native-sharing.md#known-problems
I need to remove ktor logging as well since it is causing crash on iOS due to ktor last release has changed coroutines pattern usage and awaitAll bug started to reproduce.
Most of the codes doesn’t change much, so you still can follow this article. All deprecated method also have been updated on the github.
Let’s start!
Project preparation
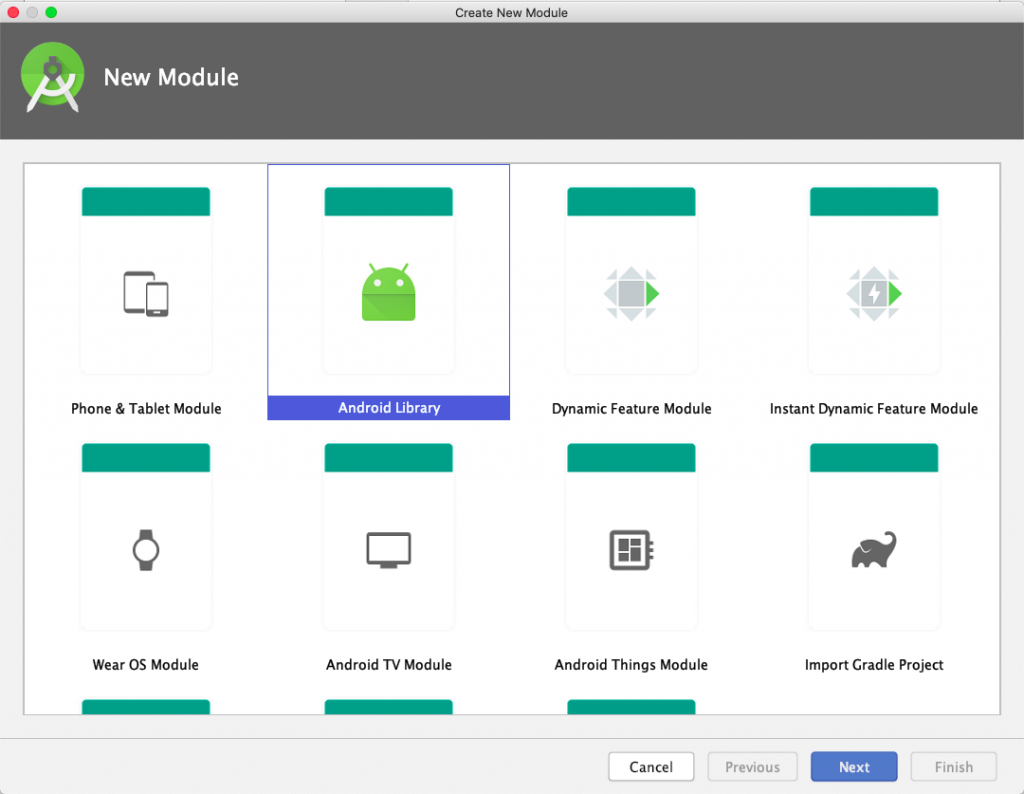
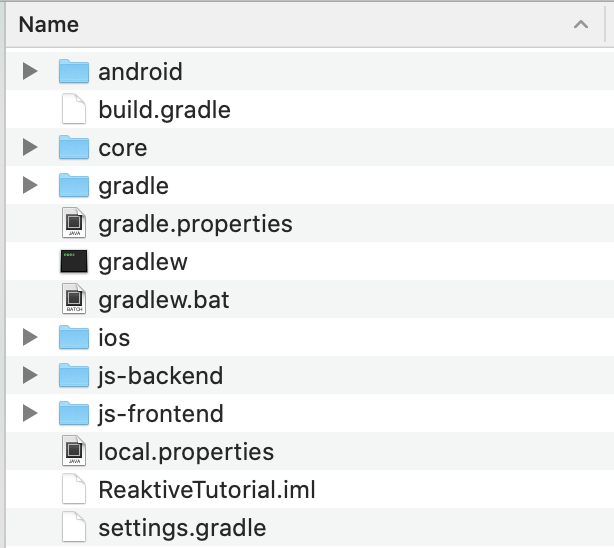
Open up your Android Studio, and create an android project, next, create new module, and choose Android Library, and lets call it: Core.
Now go to your new created project directory, and rename app folder into android folder. Close your android studio and re-open and go to settings.gradle and change your :app into :android
Note: Later if you add other platforms into the project, it is recommended that you put it at the same level with core and android directories.
Now lets start by adding dependencies into our multi platform projects. First open up projectbuild.gradle and update it by adding kotlin-serialization classpath and reaktive url into repositories. Your build.gradle should be similar to this one:
Open up your core module’s build.gradle, and delete all of its contents and replace with this one:
Then open your android build.gradle and add exclude META-INF to remove warning.
packagingOptions {
exclude 'META-INF/*.kotlin_module'
}Add implementation project(‘:core’) into your dependencies. Your android build.gradle should be look like this:
Things you need to pay attention
- Kotlin Native only support arm32 and arm64, currently there are no support for armv7 and armv7s,
- In order to bring obj-c/swift generic supports, you should add
freeCompilerArgs.add(“-Xobjc-generics”), - We created 3 sourceSets, one is
commonMainfor our Kotlin Multiplatform and the other 2 areandroidMainandiOSMainare for platform specific codes, - Some of ktor method are marked
experimental, adduseExperimentalAnnotationto get rid of those warnings.
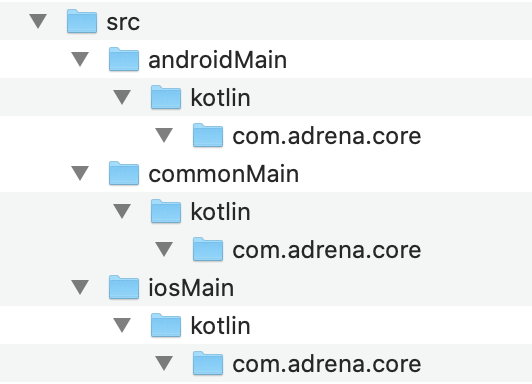
Next, removed the androidTest, main, and test directory inside core directory, create commonMain, androidMain, and iOSMain, and create kotlin as a subfolder along with a package name directory inside kotlin subfolder. Your directory structure should be like this:
Now that we’ve setup the project structure and gradle, try to build the project, and let’s continue to the next step.
Data Layer
Connecting to cloud service
We will connect to OMDb and get the movie list using ktor. API is free, you can get it from here:
https://www.omdbapi.com/apikey.aspx
We are going to search all movies contain avenger keyword with this url: http://www.omdbapi.com/?s=avenger&apikey=xxxxxx
Below are the JSON responses from the API:
Now that we know the responses, we will create DTO (Data Transfer Object), domain models and a transform class to map DTO to domain models:
How it works
- We create DTO to serialise JSON responses from API into model,
- Next, we create domain model which will be used across our multi platform project. In this example this might be seems redundant because both DTO and domain model have the same data structure, however in real life app, your domain model might have different structure or data types,
- Last, we create transform class to transform DTO into Domain Model.
Now after we’ve prepared our data models, we create Service Interface and its implementation class to connect to API server and get the result.
How it works
- First we create Service Interface to provide abstraction,
- After that, we setup http client using
ktor, we use build-in install method to install json feature and use default kotlin serializer. We also install logging feature to log the API request & response, - Next, we prepare
apiUrlinHttpRequestBuilder.apiUrlby addingapiKeyto host url, - inside override suspend fun execute, we call OMDb url by passing search parameter and serialise the response text to our MoviesResponse and then transform it to our domain model.
Note: we’re using suspend function because its required when using ktor as most of its methods are based on Coroutines.
Update on 20 Sept 2020:
HttpResponsehas been deprecated on ktor 1.4.0, use the following code to get response from API.
Repository
Repositories hide the details from outside on how the data is stored and retrieved. Data store can be SQL, Cloud or even file. Connection to and from data layer should only via repository.
Let’s create a repository interface.
Repository implementation
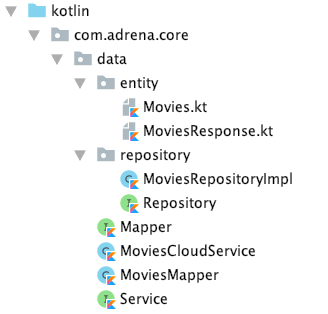
Now that we’ve finished preparing the data layer, your directory structure should be similar to this:
Domain Layer
Use case
Use cases contains business logic, they can contain one or more repositories and provide result into our view.
Our use case for this tutorial are pretty simple contains only 1 repository to get the list we need:
Implementation
Presentation Layer
Coroutines Interop
ktor make heavy use of coroutines to do asynchronous task, and we have to find a way to transform suspend fun into observable stream. Luckily Reaktive provide a Coroutines interop for us to do that. You can add this implemention inside your core’s multi platform build.gradle.
implementation ‘com.badoo.reaktive:coroutines-interop:<latest-version>’
During example creation for iOS, i’ve found a problem that ktor does not return any response code using latest coroutines-interop v1.0.0. If you’ve experienced similar problem, you can use below code as a temporary fix.
Update on 20 Sept 2020:
- For kotlin 1.4.0, use
singleFromCoroutinefromcoroutines-interop:x.x.x-nmtcinstead of above code to prevent crash on iOS.
Update on 20 Sept 2020:
- For kotlin 1.4.0, use
singleFromCoroutinefromcoroutines-interop:x.x.x-nmtcinstead of above code to prevent crash on iOS
ViewModel
ViewModel represent the data that we want to display on our view. In this example, our view model will return list of movies.
Implementation
How it works
- We created view model Interface exposing 2 inputs: one is for getting list of movies and the other one is to load more list, and 2 outputs: one is for showing loading indicator and another is for showing the result.
Inputsrepresent any interaction or input from the view, whileOutputsrepresent changes from view model that the view has to display. Communication from/to view model can only happened via this exposed inputs and outputs, - All view model’s processes should only happen on init constructor. We are using 2 publish subjects to get movie list, and another subject to load more movies. Inside flatMapSingle, we are using
singleFromCoroutinemethod to transform use case’s suspend fun into Single observable. - Next we merge both streams into one observable called
result. One thing that you should pay attention is that i’ve added mapper into view model constructor to map domain model into presentation model, .e.g.: Parcelable model in Android.
Building Wrapper Class
Now that we’ve set up all layers, the last part before we moved to Android and iOS is creating a wrapper class. This class simply provide a method to access reaktive subscribe method so it is accesible on both platforms.
UI
Now we are into UI parts of tutorial, lets building an android platform to display list of movies using recycler view.
Android
Lets start creating parcelable model and its mapper.
Mapper
Next we’ll setup android activity.
Note: I won’t go into detail on how to setup adapter and view holder as its pretty straightforward process for android developer.
How its works:
- We start by lazy prepare our view model; stitching all the necessary parts starting from service, repository, use case and put them into
ListViewModelImpl, and since we’re going to use parcelable model, we also passMovieModelsMapperinto ViewModel. Alternatively you can provide this view model through dependency injection using Dagger 2 or Koin, - onCreate process are pretty common, setting up recycler view, set the adapter and scroll listener to always load more movies if they reached specific point when user scroll the list. During onCreate we also call
viewmodel.inputs.getto start downloading movie list from the API, - we dispose all subscriptions in onDestroy() to prevent memory leak,
- inside binding() methods, we subscribe to view model’s output that we care about:
loadingandresult. - After we finished downloading data, we set the movie list into the adapter.
iOS
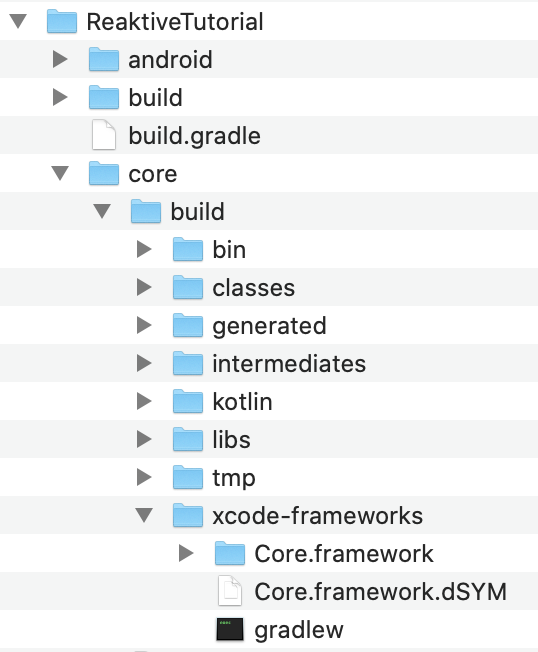
If you are using macOS platform, you can continue building Kotlin Multiplatform for iOS, let’s start by building iOS framework from gradle. Type this command inside Android Studio Terminal:
After successful build, your can check your framework inside xcode-frameworks sub directory.
Now lets open Xcode, click create new project, and save it into iOS directory
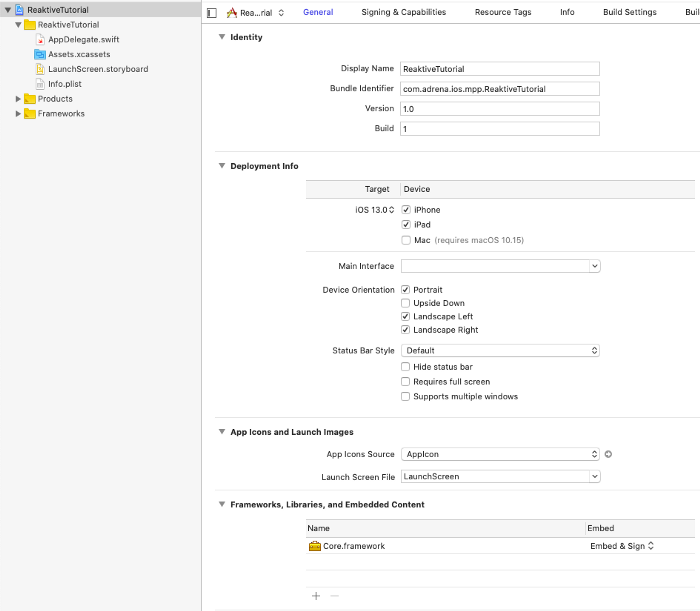
There are a couple of setup before importing framework into your projects. First click your project and go to Frameworks, Libraries, and Embedded Content, drag and drop Core.framework from xcode-frameworks directory into it.
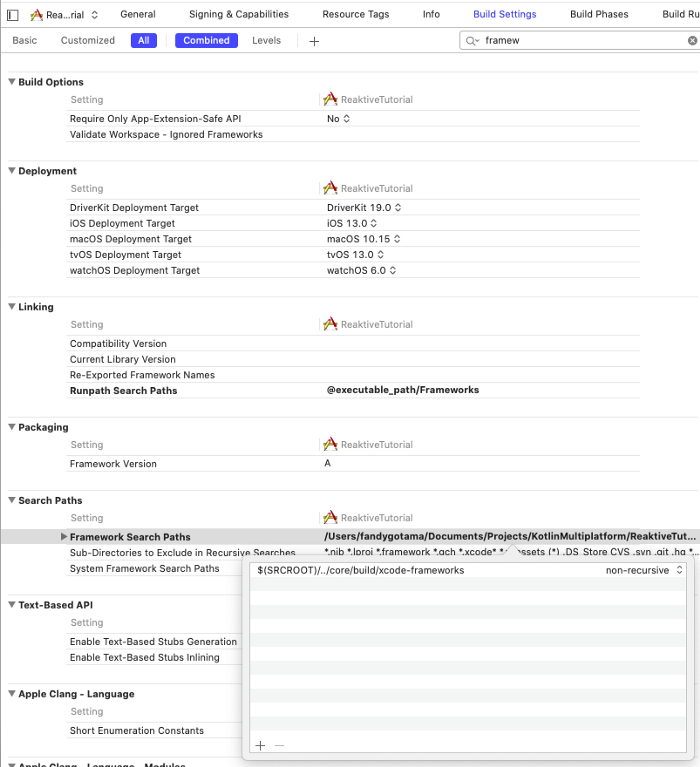
Now go to Build Settings, search Framework Search Paths and put your xcode-frameworks path. If you follow this example from beginning and use the same directory structure and name, you can type $(SRCROOT)/../core/build/xcode-frameworks
Last, go to Build Phases, add New Run Script Phase, move it below Dependencies section, and add this bash script.
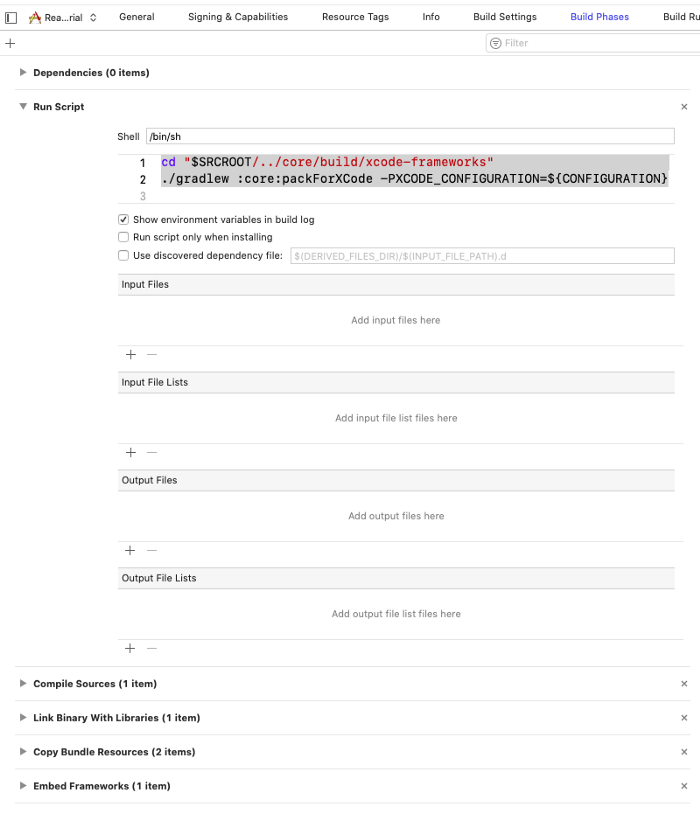
This run script will make sure that we will always get the latest framework code when building the app.
You should be able to import Core after building the project.
Next we will setup ViewController.
Again, i won’t go into detail how to setup UICollectionViewDataSource and UICollectionViewCell.
How its works:
- The process is pretty much similar to Android’s Main Activity, we setup
UIRefreshControlandUICollectionView, and lazy init the View Model. - If you take a closer look into View Model’s generic, i’m using Obj-c’s
NSStringinstead of Swift’sString. Using Swift’s String directly will give you an error ‘ListViewModelImpl’ requires that ‘String’ be a class type. This is one of the limitation that i’ve found so far using generics, - I’m passing nil into
ListViewModelImplmapper and use domain model from Kotlin Multiplatform project directly, - Inside
ViewDidLoad, we callbinding()method to subscribe into view model’s output:loadingandresult, and then at the end, we calledviewmodel.inputs.getto start downloading movie list from API, - After we’ve finished downloading the data, we make sure that the result is a movie list and set it to collection view’s data source. This is another limitation i’ve found; even though we already set
MovieasListViewModelImpl’s generic, we always get Any as a return type, - Don’t forget to make sure that your View Controller’s
deinitis called every time you pop or dismiss your View Controller
and…, we’re finished!
Thats pretty long journey 🤩, i hope you’re not getting lost and make it to last part successfully. You can stop here if you think you’ve already gotten what you wanted. However like everybody said, a good app should always give feedback in a bad / no internet connection. If you’re still have time, let’s take a look into the last part of this tutorial.
Caching
Caching is one of the important part when building a good app, and we’re very fortunate that Kotlin Multiplatform has a library called sqldelight to help us. (https://github.com/cashapp/sqldelight)
Lets start by adding sqldelight dependencies into our build.gradle.
Start by opening project’s build gradle and add a new classpath into dependencies:
Now open, core’s build.gradle, apply plugins and add sqldelight in commonMain and iOSMain
In the same core’s build.gradle add the following script:
How it works:
- We’ve added
sqldelightsupport into ourbuild.gradle, - We also set
sqldelightdatabase config inside core’sbuild.gradle.
Note: By default if not specified, sqldelight will use default Database as a name.
Next, create a directory inside commonMain by following the package name and sourceFolders we’ve setup before. Your directory structure should be like this:
Now, lets add a new file called Movie.sq, copy the sql script, save inside com.adrena.core.sql directory, and then build the project.
Note: sqldelight will automatically generate a kotlin script based on our provided sql syntax. In this example you can access insert query by calling insert()
You should see a generated kotlin code in your Android Studio similar to this:
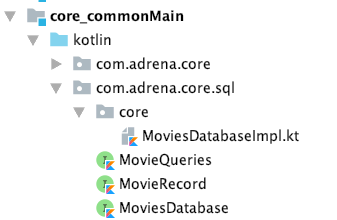
Note: if your directory is not generated after building the project, try restarting your Android Studio.
Let’s continue by creating cache sub directory inside data directory, and create a database helper class.
How it works:
- We started by creating sql file called
Movies.sqin specific package directory matches our sqldelight config inbuild.gradle, sqldelightwill auto-generate kotlin code,- We created
DatabaseHelperclass to provide access tosqldelightfrom Android and iOS. Android should provide the driver directly from Android Project itself because it need Context as parameter, while iOS will provide the driver using Kotlin NativeSqlite.
Sql caching
Start by creating caching interface and its implementation
Implementation
How it works:
- First we created cache interface as a contract to all app caches. Caching is not always sql, but can be a file or memory. By providing an interface we will make sure that any other caching mechanism in our app will works as long its follow the contract,
- We set implementation class which is pretty straight forward, insert into sql and read from sql and transform the result into movie list.
Repository class modification
Now let’s modify our repository class to return movie list from cache if available or request from API if cache is empty.
How it works:
- First we check if we have cached movie list, if not, we retrive the list from API and save it to cache.
- Now that we’re done updating our multi platform project, it’s now time to update our Android and iOS code.
Android
Add sqldelight into Android’s build.gradle
Now open Main Activity and update the following code:
Last, update your settings.gradle
How it works:
- We add
sqldelightimplementation into Androidbuild.gradle, - We setup
DatabaseHelperclass usingAndroidSqliteDriver. Please note that this approach is not recommended. dbHelper should be singleton and should not be initialized in every activity, - We updated our view model object to include cache,
- last we updated our settings.gradle with
enableFeaturePreview(‘GRADLE_METADATA’). Do not forget to update this, otherwise gradle will throw error when you try to build iOS Framework.
Try running your Android app. First time running it will fetch the movie list from OMDb, the next time you load, it will always load the list from your cache.
iOS
Run ./gradlew packForXCode and open up your Xcode project. Open your AppDelegate and add this code:
Next, open up your ViewController and update view model object:
Try running your iOS project, it should behave the same way just like Android.
Conclusions
Kotlin Multiplatform can help us build one business logic for Android and iOS, speeding up development process and help reducing unnecessary bugs because of different code base. However there’s always pros and cons when trying something new. Here what’s the list i’ve found during the creation of this tutorial.
Cons
- Kotlin Multiplatform Project is still experimental, expect a lot of refactoring if you plan to try it in your production,
- 3rd party library support for multi platform are still not much, however when creating business logic, you don’t really need a lot of library: ktor, Reaktive, sqldelight and klock are more than enough for me,
- No LiveData, no android ViewModel, you have to take care of your object lifecycle by yourself,
- obj-c/swift interop are not perfect yet,
- Debugging is hard, up until this point i’m still unable to debug (by placing breakpoint) Kotlin Multiplatform project.
Pros
- Single business logic for multiple platforms, greatly reduce development time.
As for me, this single pros beating all the cons that i mentioned above. In fact, i’m going to try multi platform on our next project. Wish me luck 😄.
Last but not least, you can get the code from github:

