
Google has done a good job when introducing Paging 3 in Android 11 which has so many features that simplified complicated process creating RecyclerView with paging.
If you’re looking for Paging Implementation using Coroutines and Flow, you can visit their code labs here
https://codelabs.developers.google.com/codelabs/android-paging/#0
This tutorial serve as alternative for other who doesn’t want to use Coroutines and prefer RxJava instead.
Paging 3 Architecture
Paging 3 was designed to follow Android Architecture Component using Repository, ViewModel and UI Layer.
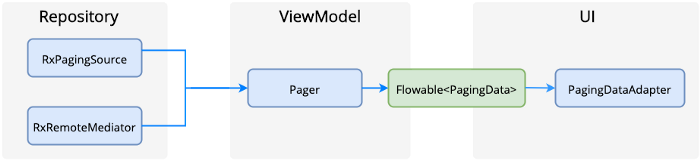
A brief explanation for each of the layer:
RxPagingSource
Use this if you only have 1 source data, e.g.: Network or Local Storage or File
RxRemoteMediator
Use this if you want to load data from network and save it to your local storage. RemoteMediator will take care of getting data for you. For example during loading data, it will check the local storage first, if no data found and next page is available, it will get data from network. RemoteMediator is using 1 single source of truth for data source, that is: your local storage.
Pager
Pager will turn PagingData from your repository into stream. In this case into Flowable or Observable.
You can also do data transformation in ViewModel. For example: you want to filter data based on specific condition or you want to add section separator.
PagingDataAdapter
PagingDataAdapter extend RecyclerView.Adapter and is specifically created to support PagingData on UI Layer. Simply call adapter.submitData(lifecycle, list) and it will handle item insertion, update and deletion for you.
Goal
In this tutorial, we’re going to connect to TMDB to get list of movies using Paging 3 approach. Here’s the final result of the app

Libraries
At the time of writing, i am using the latest version of the following libraries:
Paging: 3.0.0-alpha3
Room: 2.3.0-alpha2
Retrofit: 2.7.2
Android Studio: 4.0.1
Let’s Start!
Open up your android studio, create empty Activity. Open up your app builds.gradle and paste this code
We’re going to start the journey from Repository up to UI Layer.
Repository
Before going directly to RxPagingSource and RxRemoteMediator, lets start by preparing our Network API, model and Room Database.
Create retrofit, response, model and mapper
We are going to load list of favourite movie from TMDB using retrofit and map it to model using mapper
Now lets create MoviesResponse, Movie object and Mapper code
Here we’re creating Movies Model which has 2 inner class: Movie and MovieRemoteKeys. We are going to keep page tracking in separate table.
You can also put page tracking in one single table, in this case
Movie Table. By separating it into 2 tables we are following Separation of Concern Principle.
Next we will create Image Model class to get image based on its size.
and last, here’s the mapper.
How it works
All above steps should be pretty self explanatory since its pretty standard step to get data from API and map it into Object Model
Preparing Room Database
Lets start creating 2 Dao, one for Movies and the other one for MovieRemoteKeys
Note that we’re using PagingSource when selecting movies. Yes, Room also support Paging 3 out of the box. It will automatically select movies based on previous or next page provided without extra code!
You need to pay attention also on this code:
Make sure that your query returned the same order as your API response or you will get incorrect page result when using RxRemoteMediator
Since we’re using
RxJava, make sure you don’t accidentally usesuspendwhen creatingDAO
Next, we’re going to create Room Converters because we have custom data type in our model: Image and Date
Now, lets create our Database Class
How its works
Again all above step are pretty straight. We’re creating DAO for both Moviesand MovieRemoteKeys, create TypeConverter to convert object into sqlitedata type, and last we create Database Class.
RxPagingSource
If you only want to load data from 1 data source, e.g.: Remote, Local Storage or File, you can simply use RxPagingSource to achieve that.
RxPagingSource need us to override loadSingle and return Single stream.
How it works
In this class we are calling service to get favourite movies which also return Single , then we run it on background thread by calling .subscribeOn(Schedulers.io()), and we map the response into Movies Model, last we map it again into LoadResult.Page
LoadResult have 2 type parameters, the first one is the page navigation key type, usually Int or String, and the second one are the data itself, that is: list of movies.
In LoadResult.Page we assign list of movies into first parameters, and prevKey & nextKey parameter to track page.
TMDB use
querystring page=1, page=2, page=3to navigate to next or previous page, so we can simply substract current page by 1 to go to previous page, and add current page by 1 to go to next page. If your API is using different type of navigation, you can always change it toprevKey = movies.prevKey and nextKey = movies.nextKey
RxRemoteMediator
You can use RxRemoteMediator as alternatives if you want to use multiple layers of data, such as: Network and Local Storage. RxRemoteMediator is using your local storage as 1 single source of truth to present data. Which means all data from network will be saved to your local storage first and then shown to user via that storage.
Same as RxPagingSource, RxRemoteMediator need us to override loadSingle and return Single stream. The different between RxPagingSource is that we need to keep track of the page and also insert the result from API into database. Let’s run through the code.
How it works
- We convert
loadTypeintoSingleby callingSingle.just - We want all process to run in background thread by calling
.subscribeOn(Schedulers.io()) - LoadType have 3 enum values:
REFRESH,PREPENDandAPPEND.REFRESHwill be called during initial load, or every-time the data need to be refreshed.PREPENDwill be called if user scroll to near top andAPPENDwill be called if user scroll to near bottom, depends on paging configuration. Here in this code we’re getting page variable based on whichenumprovided to us fromMovie Table. getRemoteKeyClosesToCurrentPositionwill search for page closes to current scroll position, if returnnullmeans this is the initial page loadgetRemoteKeyForFirstItemwill try to get first remote key found in the first movie data. This method will be called duringPREPENDevent, means that we should provide previous key to load movie data before scroll to top endedgetRemoteKeyForLastItemwill try to get last remote key found in the last movie data. This method will be called duringAPPENDevent, means that we should provide next key to load movie data before scroll to bottom ended- If
remoteKeys.prevKeyorremoteKeys.nextKeyisnullwe will assume that user already reached the end of the page and just returnINVALID_PAGE - After getting the key, we call
flatmapto get response from API. But first we validate the page whether it’s a valid page or not, if not just tell theMediatorthat the list has ended - Call to API is the same as
PagingSource. We call the service, map it toMovies Model, and then insert the result to database by callinginsertToDband tellMediatorif this is the end of a page or not by callingMediatorResult.Success - during insertion, we will check if
loadTypeenum isREFRESHor not. If yes, we clear the both table, and then we continue to insertPagingDataintoMovieRemoteKeys TableandMovieintoMovies Table - Any exception found during the process will call
MediaResult.Error
Repository
After we’ve created the Single streams, its time to setup the PagingDataand turn it into Flowable. First lets create the interface to cater our repository implementation.
Next we created a repository for RxPagingSource
Here we are creating Pager class which has public API to turn PagingDatainto Flowable Streams. We also supply the configuration during the creation. Below are the list of configuration available:
pageSize: Mandatory, if your API hasquery stringto show how many data will be shown use this to pass it to API. In this tutorial TMDB doesn’t have the feature to load list of movies using custompageSize, so we use their default value.enablePlaceholders: Defines whetherPagingDatamay display null placeholders ifPagingSourceprovides themmaxSize: DefaultMAX_SIZE_UNBOUNDED. Defines the maximum number of items that may be loaded intoPagingDatabefore pages should be dropped. Value must be at leastpageSize + (2 * prefetchDistance)prefetchDistance: Prefetch distance which defines how far from the edge of loaded content an access must be to trigger further loading. Typically should be set several times the number of visible items onscreeninitialLoadSize: Default ispageSize * 3. Defines requested load size for initial load fromPagingSource, typically larger thanpageSize, so on first load data there’s a large enough range of content loaded to cover small scrolls.jumpThreshold: Default isCOUNT_UNDEFINED. Threshold for number of items scrolled outside the bounds of loaded items to trigger invalidate.
Next we create repository for RxRemoteMediator
The setup is almost the same with RxPagingSource’s Repository, the only differences is we need to add remoteMediator and provide our database as pagingSourceFactory
We’re done in repository layer, lets move to ViewModel
ViewModel
in ViewModel we can do data transformation if needed and cache the transforamtion so it won’t be re-run during configuration change.
In this tutorial we only want to show all movies with posters. Here’s how you can do it using map and filter.
Thats all in ViewModel part, now lets move to UI Layer
UI
PagingDataAdapter
PagingDataAdapter are created to make implementation of Paging 3 very easy in this layer. Most of the time using PagingDataAdapter is enough, however if you want to do a lot of custom modification, you can always create your own Adapter by implementing AsyncPagingDataDiffer manually.
Create a class implementing PagingDataAdapter by providing COMPARATOR as constructor parameter. Adapter are using COMPARATOR to index list and item diffing. The rest of implementations are the same as standard Adapter.
Below are the layout and ViewHolder code
I’m using coil to display the image btw 🙂
How it works
In this UI Layer we created Adapter that extend PagingDataAdapter and use MovieGridViewHolder to display the movie poster, nothing fancy.
Now let’s move to the last part of tutorial.
Activity / Fragment
As you can see from the code above, the implementation is very clean, no over complicated logic to show next or previous page. All you have to do is subscribe to the ViewModel and call mAdapter.submitData by passing fragment’s lifecycle and the PagingData
Conclusions
Paging 3 is great, although its rewritten completely using Coroutines and Flow, we still can use it using RxJava.
The implementation is very clear using Android Architecture Component and create a standard for all developers who want to implement Paging in their RecyclerView.
You can check full source code here:
https://github.com/gotamafandy/paging3
Look for Rx dir for RxJava and Flow for Coroutines

